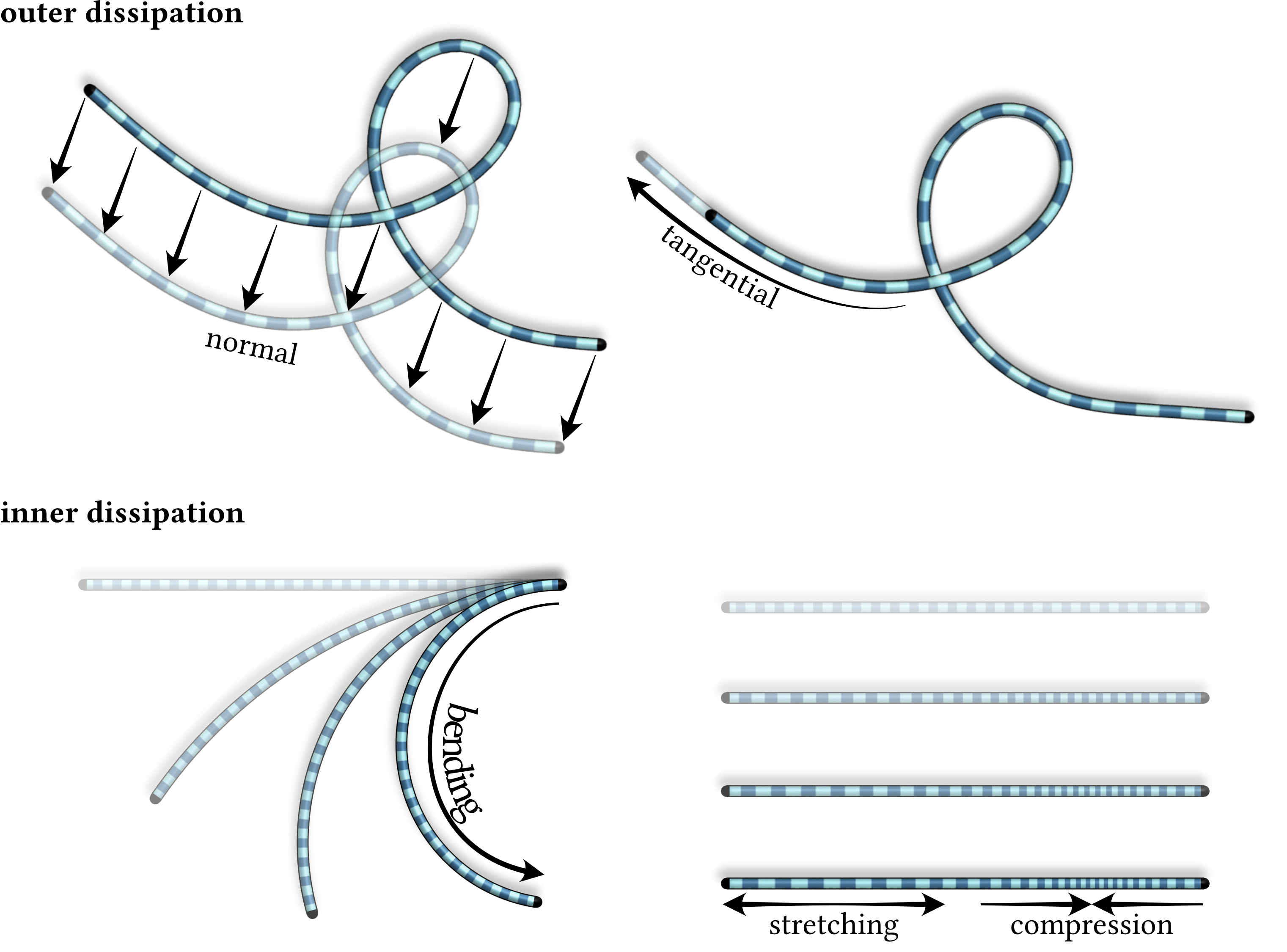
We propose a geometric model for optimal shape-change-induced motions of slender locomotors, e.g., snakes slithering on sand. In these scenarios, the motion of a body in world coordinates is completely determined by the sequence of shapes it assumes. Specifically, we formulate Lagrangian least-dissipation principles as boundary value problems whose solutions are given by sub-Riemannian geodesics. Notably, our geometric model accounts not only for the energy dissipated by the body's displacement through the environment, but also for the energy dissipated by the animal's metabolism or a robot's actuators to induce shape changes such as bending and stretching, thus capturing overall locomotion efficiency. Our continuous model, together with a consistent time and space discretization, enables numerical computation of sub-Riemannian geodesics for three different types of boundary conditions, i.e., fixing initial and target body, restricting to cyclic motion, or solely prescribing body displacement and orientation. The resulting optimal deformation gaits qualitatively match observed motion trajectories of organisms such as snakes and spermatozoa, as well as known optimality results for low-dimensional systems such as Purcell's swimmers. Moreover, being geometrically less rigid than previous frameworks, our model enables new insights into locomotion mechanisms of, e.g., generalized Purcell's swimmers. The code is publicly available.
|